Dust resulting from wear on the linings and accumulating on brake components may contain asbestos that is hazardous to health. Do not blow this dust out with compressed air or inhale it! Do not use gasoline-based solvents to remove dust. Dust should be washed off with a special brake system cleaner or methyl alcohol in a drain container. After wiping brake system components with a damp cloth, keep the cloth and the contents of the drain container in a closed and labeled container. In the future, if possible, try to use asbestos-free components.
In addition to checks at regular intervals, the condition of the brake mechanisms should be carried out each time the wheels are removed or when signs of a malfunction appear in the system. To ensure driving safety, the brake check procedures described below are the most important of all vehicle maintenance procedures you perform.
Signs of problems in the brake system
1. Disc brakes may have built-in lining wear indicators that indicate that lining wear has reached a critical value. In this case, the pads should be changed immediately, otherwise the brake discs will be damaged and they will require costly repairs.
2. Any of the following symptoms may indicate a potential defect in the brake system:
- a) When depressing the brake pedal, the car "leads away" one way
- b) Brakes make screeching or squealing noises when braking
- c) Brake pedal has excessive travel
- d) Brake pedal pulsing (this is normal only when the ABS system is working)
- e) Brake fluid leaks (usually on the inside of a tire or wheel)
3. If at least one of these signs is found, inspect the brake system immediately.
Brake lines and hoses
The brake system mainly uses steel brake pipes, with the exception of flexible reinforced hoses at the front wheels and as connections at the rear axle. Regular inspection of all these lines is very important.
4. Park your vehicle on level ground and turn off the engine. Remove wheel covers. Loosen but do not remove all four wheel bolts.
5. Jack up the vehicle and place it securely on jack stands.
6. Remove the wheels (refer to Section Wheel rotation and replacement).
7. Check all brake lines and hoses for cracks and abrasions in their outer coating, leaks, swelling and deformation. Check the brake hoses at the front and rear of the vehicle for signs of softening, cracking, deformation, or wear due to rubbing against other components. Check all fittings for signs of leaks and make sure all bolts and brake hose clamps are secure.
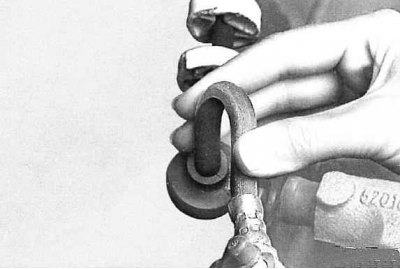
8. Bend the brake hose back and forth with your hands to check for damage. Hoses should not be twisted. Follow the direction of the colored line marked on the hose.
9. Turn a steering wheel to the right and to the left against the stop. The hoses must not touch the structural elements of the vehicle.
10. If fluid leaks or damage is found, repair them immediately. For a more detailed description of the procedure for repairing the brake system, refer to Chapter Brake system.
Checking the thickness of the brake pads
When the brake pads of the front and rear brakes are worn out, the indicator on the instrument panel lights up. In this case, it is necessary to urgently replace the brake pads.
The operation of lifting and placing the vehicle on stands is dangerous! Therefore, before carrying out the operation, read Section Jacking and towing
11. Mark with paint the position of the wheels relative to the hub. This will allow the balanced wheels to be returned to their original position during reassembly. Loosen the wheel bolts with the vehicle on the ground. Raise the car, put it on stands and remove the wheels.
Disc brakes
12. Visually check the thickness of the pads without a metal plate, looking from above through the caliper.
13. In addition, check the thickness of the outer shoe from the side. The wear limit of the front and rear brake pads is reached when the pad thickness is 3 mm.
14. In doubtful cases, remove the pads and measure the thickness with a caliper. When the wear limit is reached, the pads should be replaced. In this case, all four pads of one axle should be replaced, even if only one pad has reached the wear limit.
Based on experience, it is known that 1 mm of disc brake pad wear corresponds to 1000 km of run. This corresponds to unfavorable operating conditions. During normal use of the car, the life of the pads is much longer. With pad thickness of 5.0 mm (without backing plate) the block can still be used for a run of 2000 km.
15. Check up, whether the support has traces of leaks of a brake liquid. If there is a leak, immediately hand over the caliper for repair.
16. Visually check the brake discs on the inside and outside for scoring, corrosion damage and cracks. Replace disks if necessary.
Parking brake
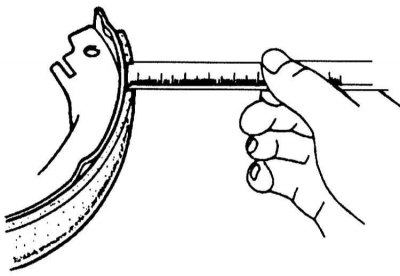
17. The parking brake pads can be visually inspected after removing the service brake disc. The wear limit is reached when the pad thickness at its thinnest point is 1.5 mm.
18. If the wear limit is reached, the pads must be replaced. Be sure to replace all pads of one axle, refer to Section Removal and installation of parking brake pads.
19. Establish wheels so that the markings put at removal coincided. Pre-lubricate with a thin layer of bearing grease the centering belt of the wheel disk on the hub. Do not grease wheel bolts. Rusted bolts must be replaced. Install the wheels and tighten the mounting bolts. Lower the vehicle onto the wheels and tighten the bolts crosswise to 100 Nm.
Checking the functioning of the parking brake
The parking brake is a cable operated drum brake. The drum is built into the rear brake discs. Since the parking brake pad wear is negligible, corrosion damage or contamination of the brake pads may occur. Therefore, before checking the parking brake, it is recommended to run it in as follows:
20. Apply the parking brake gently from 40 km/h on a deserted street or parking lot like this. Without changing speed, apply the parking brake one more tooth and drive another 400 m. Release the brake and allow it to cool.
The operation of lifting and placing the vehicle on stands is dangerous! Therefore, before carrying out the operation, read Section Jacking and towing.
21. Raise and place the rear of the vehicle on stands. The wheels must be above the ground at a height of at least 2 cm.
22. Set the parking brake one click and rotate the rear wheels. The wheels should turn freely, the brakes should not work.
23. When cocking the brake to 10 clicks, the wheels should be braked completely.
24. Otherwise, adjust the parking brake, refer to Section Parking brake adjustment.
25. Lower the car on wheels.
