BMW 3 Series E36 car engine ignition system
Ignition system. General information
The ignition system generates an ignition spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders at a certain moment. To produce a spark of sufficient power...
The ignition system generates an ignition spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders at a certain moment. To produce a spark of sufficient power...
Engines with no moving parts ignition system (all engines except 316i, 318i before August 1993)
The operation of the spark plugs is controlled without moving elements only from the control unit, there is no mechanical ignition distributor. Thanks to...
The operation of the spark plugs is controlled without moving elements only from the control unit, there is no mechanical ignition distributor. Thanks to...
Functioning of the parametric ignition system
The ignition system, like the fuel injection system, is controlled by a common central electronic circuit operating using a parameter field (DME = Digital...
The ignition system, like the fuel injection system, is controlled by a common central electronic circuit operating using a parameter field (DME = Digital...
Safety measures when working with the ignition system
In electronic ignition systems, high voltage reaches 4000 volts. Under adverse conditions, such as high humidity in the engine compartment, voltage peaks can...
In electronic ignition systems, high voltage reaches 4000 volts. Under adverse conditions, such as high humidity in the engine compartment, voltage peaks can...
Ignition timing check
Attention: The ignition timing is controlled by the control unit and can only be checked, not set. The current position is determined by two sensors (one on...
Attention: The ignition timing is controlled by the control unit and can only be checked, not set. The current position is determined by two sensors (one on...
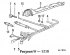
Removal and installation of a cover of the distributor/runner of the distributor
Withdrawal Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the electronic memory devices, such as...
Withdrawal Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the electronic memory devices, such as...
Checking the ignition wires
Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the electronic memory devices, such as the engine...
Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the electronic memory devices, such as the engine...
Checking the ignition coil
The ignition coil is checked with an ohmmeter. Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the...
The ignition coil is checked with an ohmmeter. Disconnect the ground wire from the battery. Attention: When the battery is disconnected, the information in the...
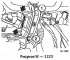
Checking and replacing the pulse sensor
The DME control unit receives information about the speed from the pulse sensor located on the gear behind the crankshaft belt pulley. The second sensor on the...
The DME control unit receives information about the speed from the pulse sensor located on the gear behind the crankshaft belt pulley. The second sensor on the...
Removing and installing the DME control unit
Attention: Each control unit is programmed for certain basic parameters, which are only average values. The control unit receives from sensors different input...
Attention: Each control unit is programmed for certain basic parameters, which are only average values. The control unit receives from sensors different input...
Spark plug
The spark plug consists of a central electrode, an insulator with a housing and a ground electrode. The mass electrode is hermetically fixed in the insulator,...
The spark plug consists of a central electrode, an insulator with a housing and a ground electrode. The mass electrode is hermetically fixed in the insulator,...
Diagnostics of malfunctions of system of ignition
* ) Applies only to models 316i, 318i built before August 1993. Other gasoline engines have an ignition system without moving parts and without an ignition...
* ) Applies only to models 316i, 318i built before August 1993. Other gasoline engines have an ignition system without moving parts and without an ignition...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections for other types of BMW cars:
Power unit: Ignition system BMW 5 Series E34 (1988-1996)
Power unit: Ignition and control systems BMW 7 Series E38 (1994-2001)
Power unit: Ignition system BMW 5 Series E34 (1988-1996)
Power unit: Ignition and control systems BMW 7 Series E38 (1994-2001)
Share information:
- General information
- Manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Power system (gasoline)
- Injection system (gasoline)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Ignition system
- Charge and launch systems
- Transmission
- Car gearbox
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Suspension front and rear
- Steering
- Body
- Body care and repair
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Troubleshooting
- Lighting and signaling
- Equipment and devices
- Heater and air conditioner
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Manual
- Repair on the road
- Weekly checks
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- 4 cylinder engines
- 6 cylinder engines
- Engine overhaul
- Cooling and heating
- Fuel and exhaust system
- Starting and charging system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Cardan and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Wheel suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Ignition system
- Supply system
- Fuel injection system
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Front and rear axle
- Chassis
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Heating system
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
- Power unit
- M10/M20 engine
- M40 engine
- Ignition system
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Fuel injection
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox
- Front axle
- Rear axle
- Chassis
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Heating system
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Specifications
- Operation and maintenance
- 4-cylinder engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- 6-cylinder engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Supply system
- Fuel injection system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- 4-speed manual gearbox
- 5-speed manual gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Cardan and rear axle
- Chassis
- Steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits