Electrical diagrams are necessary when troubleshooting electrical equipment and when installing additional equipment; according to the schemes, the passage of signals and the laying of cables are traced. The corresponding current circuit must necessarily be closed, otherwise no electric current will flow through this circuit. For example, it is not enough to apply only plus voltage to the headlights without connecting them to ground at the same time.
Therefore, the ground wire from the battery is connected to the body. However, this ground connection is often not enough, and the corresponding consumer is connected directly to ground by a ground wire, the insulation of which is usually brown. Separate current circuits include relays, switches, fuses, measuring elements, electrical, motors and other electrical elements. For correct connection, these elements are marked on their contacts.
For ordering on the electrical circuits of the interweaving of wires, individual current circuits are arranged vertically and numbered.
The vertical lines at the top are connected to a thick black line depicting the current bus in the junction box, and therefore the connection of the current loops to the power plus. At the bottom, the vertical lines connect to the horizontal line representing ground connections. The ground connection is usually made by connecting the unit body to the body, however, in some cases, ground can be supplied through a separate wire from the ground point on the body.
If a square with a number is shown in the current circuit break, the number corresponds to the number of the current circuit into which this current circuit passes.
It is best to use electrical circuits as follows:
First, according to the list of symbols, the corresponding circuit element is searched, for example, a fan switch. 8, the right column next to the name of the element indicates the corresponding current circuit with its number, which is also indicated on the electrical diagram below on a horizontal line.
To read an electrical circuit, you need to know the designations of some elements, in addition, you should know the most important symbols of electrical circuits.
Relays and control units are usually designated with the letter K. The lines inside represent the internal connections. They show how relays and other electrical and/or electronic components are connected both to each other and on the relay board.
Directly at the relay are the designations of the contacts.
Terminal designations are standardized according to DIN. The designations of the most important terminals are as follows.
Terminal 15 entered through the ignition switch. Voltage is present at the terminal only after the ignition is turned on. The wires are most often green or green with colored stripes.
Terminal 30. Battery voltage is always present at this terminal. The wires are most often red or red with colored stripes.
Terminal 31 connects to the mass. Ground wires are mostly brown. Each wire on the electrical circuit has an alphanumeric designation.
Example: 2.5 GNR.T
The numbers indicate the cross section of the wire in mm2. The letters indicate the color of the wire. If the designation consists of two groups of letters, as in this example, then the first letter sequence indicates the main color of the wire coloring (GN - green) and second (RT - red) - additional color. Since it happens that wires of the same color are used in different current circuits, it is recommended to check the color combinations of the wires connected to the connection terminals.
Wires that are connected to each other by means of individual or multi-pin connectors have a digital combination in addition to the connector designation letter.
All elements on the electrical diagrams are shown in a de-energized state. The change in current direction after switching the switch is illustrated here using the example of a two-position switch.
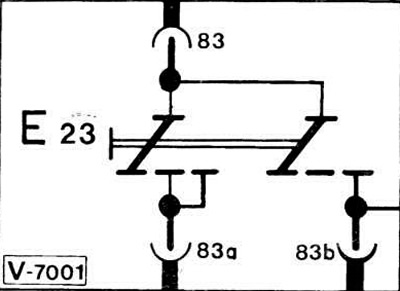
If switch E23 is set to the first position, current flows from terminal 83 through terminal 83a. In this case, the second direction of the switch is also switched, but the current circuit is not closed. Only when switched to the next position, the second direction of the switch supplies voltage from terminal 83 through an internal jumper to terminal 83b. In this case, the first direction of the switch continues to connect terminal 83 to terminal 83a.
With complex schemes of operation of switches (e.g. light switch) each relevant functional part is shown separately. The unity of the circuit breaker assembly is also expressed in its numbering.
Deciphering the designations of the color coloring of wires
- BL - blue
- BR - brown
- GE - yellow
- GN - green
- GR - gray
- RT - red
- SW - black
- VI - purple
- WS - white
- TR - transparent
- RS - pink
- OR - orange
Designations of the most important elements
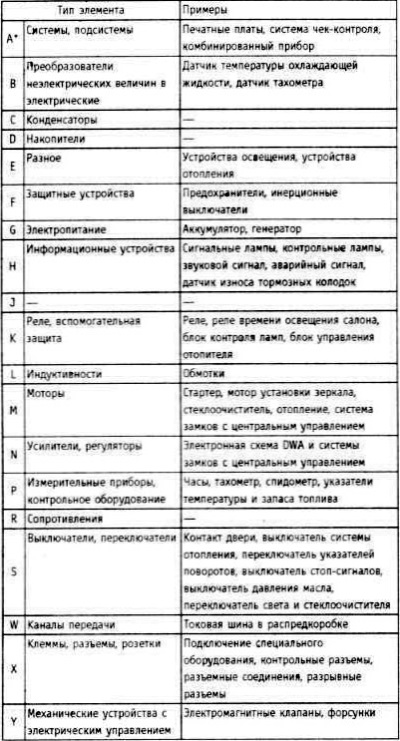
* For precise indication, alphabetic designations are supplemented with ordinal numbering.
Example:
- S5 Light switch
- 55.1 Instrument illumination switch
- 55.2 Parking light and license plate light switch
- 55.3 Headlight switch
Individual elements are discussed in the explanations to the circuit diagrams for groups with the same letter designation. The number behind the element reflects the location of the element, that is, the current circuit in which this element is located.
Example: H 17 Brake light right
- H - Designation of a group of elements (cm. «Designations of the most important elements»)
- 17 - Current number
Stoplight right - Name of the element
- 130 - Position in the current loop (at the bottom on the negative bus)
- 130 in a rectangle - the place of connection to the negative bus
